sulfo-Cyanine3 amine
| Cat. # | Quantity | Price | Lead time | Buy this product |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 113C0 | 1 mg | $115 | in stock | |
| 213C0 | 5 mg | $285 | in stock | |
| 413C0 | 25 mg |
$680
|
in stock | |
| 513C0 | 50 mg |
$1270
|
in stock | |
| 613C0 | 100 mg |
$1990
|
in stock |

A water-soluble dye with an amino group that is useful for the conjugation with electrophiles and for enzymatic transamination labeling.
sulfo-Cyanine3 is a sulfonated analog of Cy3®, which is compatible with various fluorescence measuring equipment. The dye is highly photostable. It is also easily detectable by the naked eye.
Sulfo-Cy3 absorbance and emission spectra

Customers also purchased with this product
Cyanine5 DBCO
Cyanine5 dye with dibenzocyclooctyne (DBCO) functional group for copper-free click chemistry.sulfo-Cyanine3 NHS ester
Water soluble sulfo-Cyanine3 SE activated ester for amino-biomolecule labeling.BDP TMR amine
BDP TMR amine is an amino dye for TAMRA channel. The dye possesses bright fluorescence and is well suitable for the fluorescence polarization assays.get free express delivery
General properties
| Appearance: | dark red solid |
| Molecular weight: | 714.94 |
| CAS number: | 2183440-43-7 |
| Molecular formula: | C36H50N4O7S2 |
| IUPAC name: | 3H-Indolium, 1-[6-[(6-aminohexyl)amino]-6-oxohexyl]-2-[3-(1,3-dihydro-1,3,3-trimethyl-5-sulfo-2H-indol-2-ylidene)-1-propen-1-yl]-3,3-dimethyl-5-sulfo-, inner salt |
| Solubility: | well soluble in water (0.49 M = 350 g/L), alcohols, DMSO, DMF |
| Quality control: | NMR 1H, HPLC-MS (95%) |
| Storage conditions: | Storage: 24 months after receival at -20°C in the dark. Transportation: at room temperature for up to 3 weeks. Avoid prolonged exposure to light. Desiccate. |
| MSDS: | Download |
| Product specifications |
Spectral properties
| Excitation/absorption maximum, nm: | 548 |
| ε, L⋅mol−1⋅cm−1: | 162000 |
| Emission maximum, nm: | 563 |
| Fluorescence quantum yield: | 0.1 |
| CF260: | 0.03 |
| CF280: | 0.06 |
Product citations
- Henry, W.S.; Müller, S.; Yang, J.-S.; Innes-Gold, S.; Das, S.; Reinhardt, F.; Sigmund, K.; Phadnis, V.V.; Wan, Z.; Eaton, E.; Sampaio, J.L.; Bell, G.W.; Viravalli, A.; Hammond, P.T.; Kamm, R.D.; Cohen, A.E.; Boehnke, N.; Hsu, V.W.; Levental, K.R.; Rodriguez, R.; Weinberg, R.A. Ether lipids influence cancer cell fate by modulating iron uptake. bioRxiv, 2024, preprint. doi: 10.1101/2024.03.20.585922
- Bos, I.; Timmerman, M.; Sprakel, J. FRET-Based Determination of the Exchange Dynamics of Complex Coacervate Core Micelles. Macromolecules, 2021, 54(1), 398–411. doi: 10.1021/acs.macromol.0c02387
- Zhang, Q.; Scigliano, A.; Biver, T.; Pucci, A.; Swager, T.M. Interfacial Bioconjugation on Emulsion Droplet for Biosensors. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 2018, 26(19), 5307–5313. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2018.04.020
- Sobotzki, N.; Schafroth, M.A.; Rudnicka, A.; Koetemann, A.; Marty, F.; Goetze, S.; Yamauchi, Y.; Carreira, E.M.; Wollscheid, B. HATRIC-based identification of receptors for orphan ligands. Nature Communications, 2018, 9, 1519. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03936-z
The count of items is incorrect.












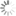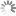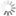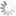
 $
$ 
